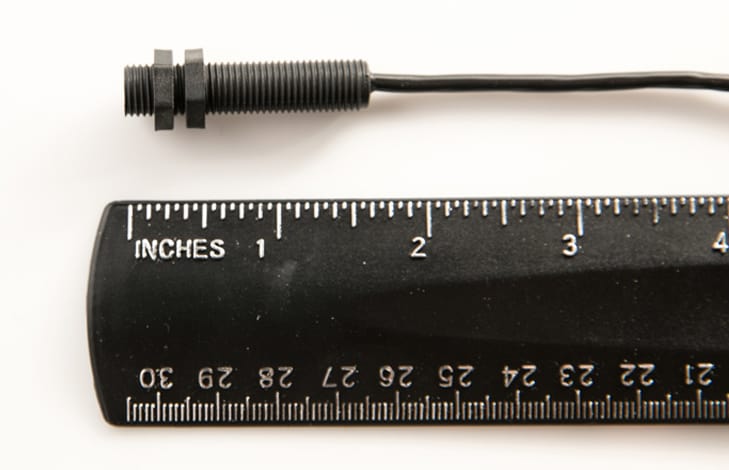
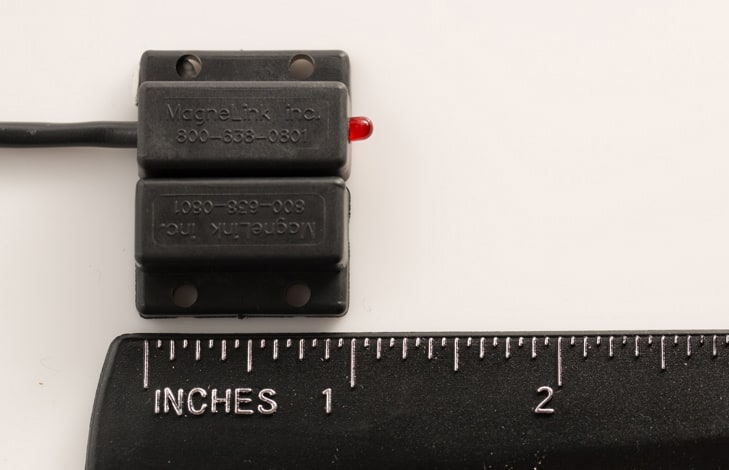
A hall switch uses a Hall Effect Sensor—a transducer that can change the output of its voltage with the application of a magnetic field. Once combined with circuitry, the Hall Effect Sensor turns the circuit on and off, based on changes in the magnetic field. Known for their high levels of precision and accuracy, hall switches can even be programmed to actuate the switch at certain magnetic fields.
Typically, hall switches are used in low DC voltage circuits, working best with small loads. These switches are commonly found in home appliances that require high-speed sensors, such as the washer and dryer. Hall switches are also commonly used by automotive manufacturers for seatbelt buckle detection, detecting the speed of the gear shifting in the car’s transmission while in operation, and to detect fluid levels. The advantage to Hall switches is that they do not use any magnetic reed contacts, so they are less vulnerable to mechanical abuse. However, they do require a steady power supply to operate properly.
To learn more about our Hall switches and their applications, contact us.